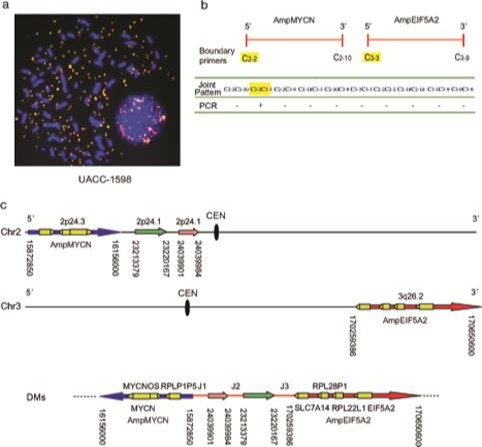
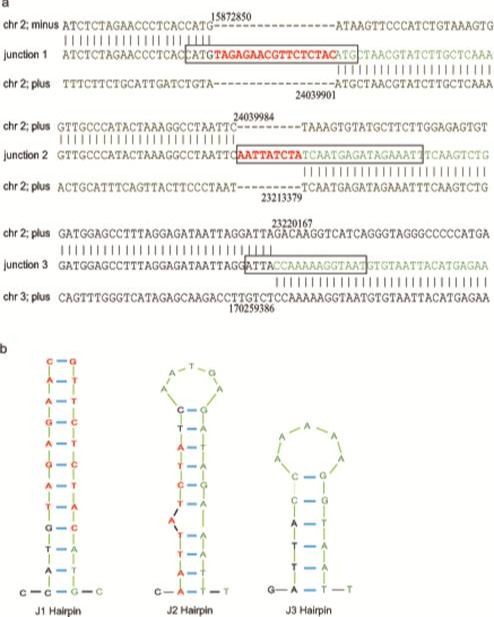
A novelty research article entitled “De novo-generated small palindromes are characteristic of amplicon boundary junction of double minutes” has been published on International Journal of Cancer. The contributors, Professor Fu Songbin and his team members, Laboratory of Medical Genetics of Harbin Medical University, revealed the structure and molecular mechanism of double minutes (DMs).
This work was in collaboration with Dr. Guan Xin-Yuan (Department of Clinical Oncology, University of Hong Kong, China), Dr. Wang Mingrong (State Key Laboratory of Molecular Oncology, Cancer Institute (Hospital), Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, China), and Dr. Ki-Young Lee (Department of Cell Biology & Anatomy, University of Calgary, Canada).
Gene amplification is a very common phenomenon in many types of human cancers, related with the initiation and development of cancer, chemotherapy resistance and worse prognosis. DMs are the ultimate cytogenetic manifestation of extrachromosomal gene amplification in cancer cells. The molecular mechanisms governing formation of DMs in human cancer are still poorly understood.
By analyzing the molecular structure of DMs in a human ovarian cancer cell line together with some published data in other cancer types, the researchers have revealed de novo creation of small palindromic sequences (which do not exist naturally) surrounding the breakpoints is a common characteristic of amplicon junction sequences in human cancers. They propose de novo generation of palindromes is involved in the amplicon rejoining process by a possible novel DNA repair machinery in concert with the non-homologous end joining pathway. In addition, the de novo generation of palindromes also mediates palindromic amplification and DMs formation.
This work was supported by the Program for Changjiang Scholars and Innovative Research Team in University, the International Science & Technology Cooperation Program of China, National Basic Research Program of China, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the New Century Support Program for the Excellent Scholar, Ministry of Education of China.
Publication link: http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/ijc.28084/abstract